Is your computer running slow? Upgrading to an SSD could be the solution.
Choosing the right type of SSD can significantly impact your computer’s performance and reliability. SATA SSDs are affordable and widely compatible while NVMe SSDs offer higher performance and lower latency.
Ultimately, the best SSD for your needs depends on your specific requirements and budget. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each type, you can make an informed decision and enhance your computing experience.
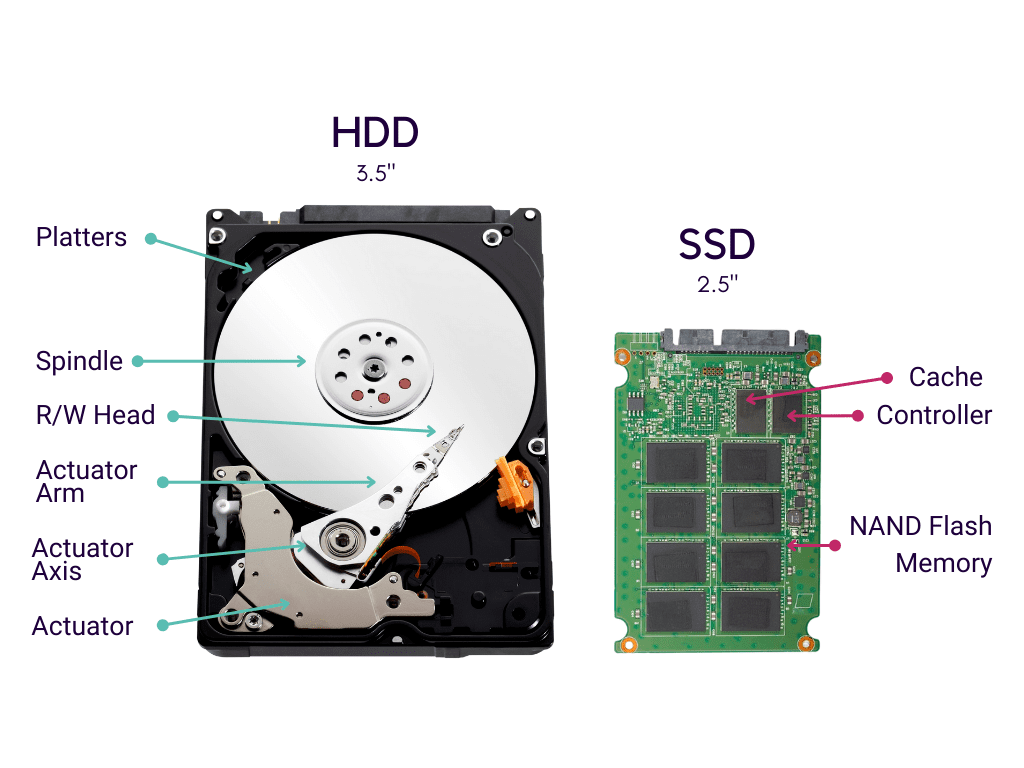
What is a Hard Disk Drive (HDD)?
A Hard Disk Drive (HDD) is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage. It consists of one or more rigid, rapidly rotating platters coated with magnetic material. An HDD uses the Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI) mode for communication, designed around 2004 to enhance the performance and utility of SATA-connected storage devices.
HDDs, using AHCI, introduced a single storage request queue with a depth of up to 32 commands. While this improved HDD performance, it later became a bottleneck for SSD technology. For example, HDDs might achieve up to 200 input/output operations per second (IOPS), whereas SATA-based SSDs can reach up to 100,000 IOPS but are limited by the SATA bus.
For example, an office worker using an HDD on their desktop might experience slower boot times and longer load times for applications compared to an SSD, making everyday tasks feel sluggish.

What is a Solid-State Drive (SSD)?
A Solid-State Drive (SSD) is a type of storage device that uses non-volatile flash memory to store persistent data. Unlike HDDs, SSDs have no moving parts, making them faster and more reliable. SSDs replace traditional HDDs in computers, providing rapid boot times, faster program loading, and quicker file saving.
Different Types of SSDs
SSDs come in various types, each suited for different needs and applications:
1. SATA SSDs: These are the most common type of SSDs, using the same interface as traditional hard drives. They offer significant speed improvements over HDDs but are limited by the SATA interface.
2. M.2 NVMe SSDs: Smaller in size than traditional SATA SSDs, M.2 NVMe SSDs are used in ultra-thin laptops, tablets, and some desktop computers. These use the NVMe interface, providing faster data transfer speeds compared to SATA SSDs. Ideal for high-performance applications like gaming, video editing, and data centres. For instance, a gamer using an NVMe SSD would notice significantly faster load times for games and quicker installations, enhancing the overall gaming experience.
3. mSATA SSDs: Mini-Serial Advanced Technology Attachment SSDs are designed for power-constrained portable devices such as notebooks and tablets.
Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) M.2
NVMe SSDs use the Non-Volatile Memory Express interface, which allows for higher data transfer speeds and lower latency compared to SATA. This makes them perfect for tasks requiring rapid access to large amounts of data, such as gaming, video editing, and data center operations.
If you were a video editor using an NVMe SSD, for example, you could work with large 4K video files without experiencing delays, speeding up the editing and rendering processes.
Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA)
SATA SSDs use the same interface as traditional hard drives, making them compatible with most laptops and desktops. While they offer substantial speed improvements over HDDs, they are limited by the SATA interface’s maximum data transfer rates.
For instance, a student upgrading their laptop from an HDD to a SATA SSD will notice quicker boot times and faster application launches, making their study sessions more efficient.

Lifespan: SSD vs. HDD
SSDs generally have a longer lifespan than HDDs. While HDDs typically last around 3-5 years due to their mechanical parts, SSDs can last up to 10 years or more since they have no moving components. Additionally, SSDs do not require defragmentation, which further extends their lifespan.
For example, a business opting for SSDs over HDDs for their office computers can expect fewer hardware failures and lower maintenance costs over time.
Read and Write Speed: HDD vs. SATA SSD vs. NVMe
The read and write speeds of storage devices vary significantly between HDDs, SATA SSDs, and NVMe SSDs. HDDs can manage speeds up to 200 IOPS, SATA SSDs can reach up to 100,000 IOPS, while NVMe SSDs can achieve speeds well beyond that, often up to 500,000 IOPS or more.
To put this into perspective, a data scientist using an NVMe SSD can run data-intensive simulations much faster compared to using an HDD or SATA SSD, leading to increased productivity.
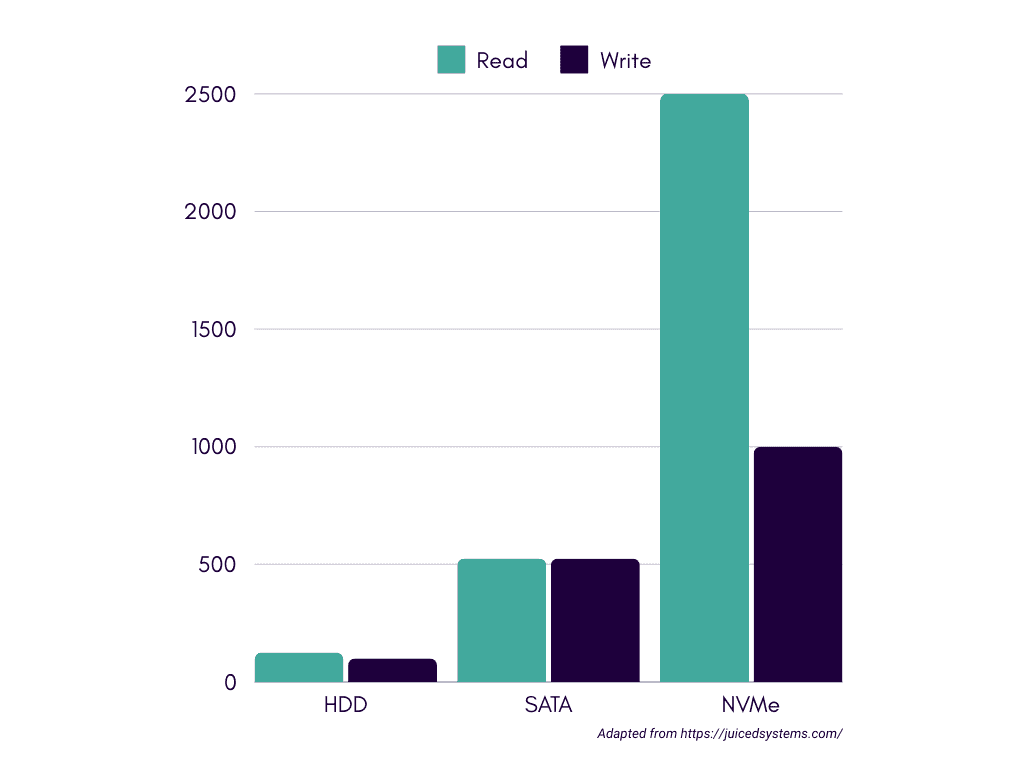
So, is your computer running slow? Upgrading to an SSD could be the solution. Choosing the right type of SSD can significantly impact your computer’s performance and reliability. SATA SSDs are affordable and widely compatible while NVMe SSDs offer higher performance and lower latency.
Ultimately, the best SSD for your needs depends on your specific requirements and budget. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each type, you can make an informed decision and enhance your computing experience.
Do you want to learn more about IT, Networking, and Cyber Security? Reach out to our team of experts, we look forward to helping you become a specialist in your field!